Torque vs horsepower is a fundamental comparison in automotive engineering, crucial for understanding vehicle performance and capabilities. Both torque and horsepower significantly influence how a vehicle accelerates, handles, and performs under various driving conditions. However, despite their interconnected nature, torque and horsepower are distinct concepts with separate implications in automotive design and functionality.
Defining Torque and Horsepower
What is Torque?
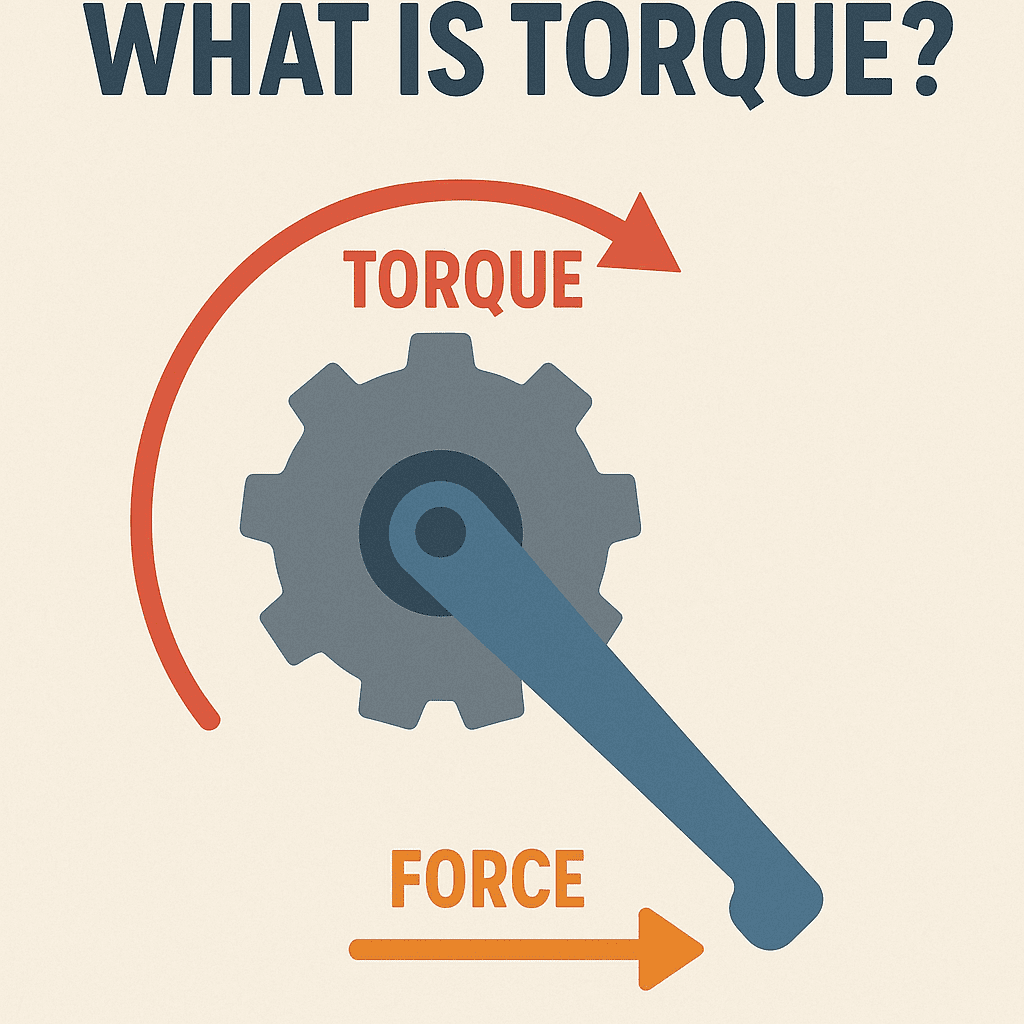
Torque represents rotational or twisting force. It is essentially the force that causes an object, such as a car wheel, to rotate around an axis. Measured in units of pound-feet (lb-ft) or Newton-meters (Nm), torque quantifies how much force is applied to an object to rotate it around an axis. For example, tightening a bolt with a wrench requires torque; the longer the wrench handle, the greater the torque applied due to increased leverage.
What is Horsepower?
Horsepower, on the other hand, is a measure of power, defined as the rate at which work is done. It quantifies how quickly torque is applied over time. Horsepower is calculated by combining torque with engine speed (RPM—revolutions per minute). The standard unit for horsepower in the United States is mechanical horsepower (hp), whereas in metric terms, power is measured in watts (W) or kilowatts (kW).
The Physics Behind Torque vs Horsepower
But First, How About A 1HP Amish Burnout?
Torque and Rotational Force
Torque is mathematically expressed as:
- Torque (τ) = Force (F) × Lever Arm Distance (r)
This formula implies that torque increases with either greater applied force or an extended distance from the pivot point. Engines generate torque through combustion, forcing pistons downward, which rotate the crankshaft and transmit rotational force to the wheels.
Horsepower and Power Output
Horsepower is derived from torque and rotational speed. The general formula for horsepower is:
- Horsepower (hp) = (Torque × RPM) / 5252
The constant 5252 arises from unit conversions and ensures units remain consistent. This formula reveals that horsepower increases either by raising torque at a given RPM or by maintaining torque as RPM increases.
Practical Implications in Vehicle Performance
Acceleration and Torque
Torque significantly impacts acceleration, especially at lower speeds. Vehicles with high torque values deliver immediate and strong acceleration from standstill, making torque critical for towing, hauling, and quick starts. Diesel engines typically produce high torque at lower RPM ranges, making them ideal for heavy-duty vehicles and trucks.
Speed and Horsepower
Horsepower, conversely, is more directly related to a vehicle’s maximum speed and high-speed performance. Vehicles with higher horsepower values generally have superior top-end speed and acceleration at higher RPMs. Sports cars and racing vehicles prioritize horsepower to achieve rapid acceleration at elevated speeds.
Real-World Examples of Torque vs Horsepower
Torque-Focused Vehicles
- Trucks and SUVs: Vehicles like the Ford F-250 or RAM 2500 emphasize torque for towing and hauling heavy loads.
- Diesel-Powered Commercial Vehicles: Engines designed for commercial trucks prioritize torque to support substantial payloads and maintain steady performance under heavy load conditions.
Horsepower-Focused Vehicles
- Sports Cars: Vehicles such as the Porsche 911 or Ferrari 488 focus on high horsepower, enabling rapid acceleration, high-speed stability, and enhanced track performance.
- Performance Motorcycles: High-horsepower motorcycles, like the Ducati Panigale V4, utilize horsepower to deliver exceptional acceleration and top speeds.
Torque vs Horsepower: Balancing Act in Automotive Design
Automotive engineers strive to balance torque and horsepower to meet specific vehicle performance goals. This balance depends on the intended use of the vehicle, customer preferences, and performance objectives. Vehicles designed for daily commuting, for instance, emphasize torque to facilitate stop-and-go driving, while high-performance vehicles prioritize horsepower for speed and acceleration.
Factors Influencing the Torque-Horsepower Balance
- Engine Design: Engine displacement, fuel delivery systems, turbocharging, and supercharging significantly influence torque and horsepower characteristics.
- Transmission Systems: Gear ratios and transmission types determine how effectively torque and horsepower are delivered to the wheels.
Misconceptions About Torque and Horsepower
Misunderstandings often arise regarding the relationship between torque and horsepower. Common misconceptions include:
- More Torque Equals Faster Car: While torque enhances acceleration from standstill, horsepower determines the vehicle’s ability to maintain acceleration at higher speeds.
- Horsepower is All That Matters: Without sufficient torque, a vehicle might struggle to accelerate effectively, especially under heavy load or uphill conditions.
Understanding the distinct roles of torque vs horsepower helps drivers appreciate vehicle specifications and performance characteristics more accurately.
Conclusion: Torque vs Horsepower in Automotive Engineering
In summary, torque vs horsepower represents a critical distinction in automotive engineering and physics. Torque measures rotational force and significantly affects initial acceleration and towing capability, while horsepower quantifies power output, influencing top speed and high-speed performance. Successful automotive design involves carefully balancing torque and horsepower to achieve desired vehicle performance outcomes. By understanding the fundamental differences between these two parameters, automotive enthusiasts, engineers, and consumers alike can better evaluate vehicles and their capabilities, making informed decisions aligned with their specific driving needs and preferences.